
started and stopped) by the creator or SYSDBA. Only one audit trace session can exist - Firebird starts it and stops it.Ĭan be managed (i.e. Each user may start as many trace sessions as he needs. Many user trace sessions may run simultaneously. Is automatically resumed by Firebird as soon as room is available. It can be different for each database or the same for all databases.Ĭould be temporarily paused by Firebird when the temporary files are full. The log file name can be set in the nf on a per-database (per-service) basis. Output is read by initiated service connection (the log starts and stops with session begin and end). The log files are not deleted by Firebird. The log is not preserved after Firebird shutdown. However the functionality of the two session types are different:Īlways initiated by the user via a special service (application or similar).Īlways initiated only by Firebird itself. The system audit is described in detail in the Firebird 2.5 Release Notes.
#Audit number on temporary id full
The template file nf, found in Firebird's root directory, contains the full list of available events, with format, rules and syntax for composing an audit trace configuration file. It is sufficiently flexible to allow different sets of events for different databases to be logged to separate log files. A configuration file contains list of traced events and points to the placement of the trace log(s) for each event. By default, the value of this parameter is empty, indicating that no system audit tracing is configured. A parameter in nf, called AuditTraceConfigFile, points to the name and location of the trace configuration file, which is consulted every time a system audit session is started.

For example, if you wish to know the number of currently active transactions inside a database, simply query the MON$TRANSACTIONS table. Nevertheless, an audit/trace does not replace the monitoring tables, because with the monitoring tables, the user can query a snapshot of the current state of a database, whereas an audit/trace can be compared with a sequential stream of logged statements. It is also possible to save filtered data as a trace log file.
Some of the supported statements include:

#Audit number on temporary id free
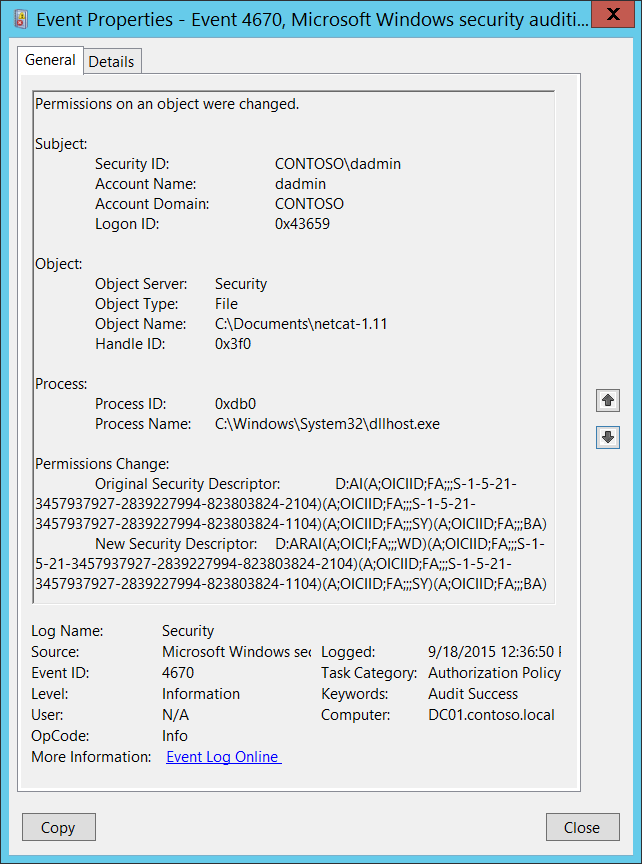
(This feature is unfortunately not included in the free IBExpert Personal Edition.) This feature enables you to look inside the Firebird engine and log various events for real-time analysis. This menu item supports the Firebird 2.5 Trace and audit services, initially developed from the TraceAPI contributed by Nickolay Samofatov that he had developed for Red Soft Database, a commercial product based on Firebird's code.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
